
Students Guide to Printing- 45

-Few objective Questions and answers-
186) What are the normal printing defects one encounter during printing ?
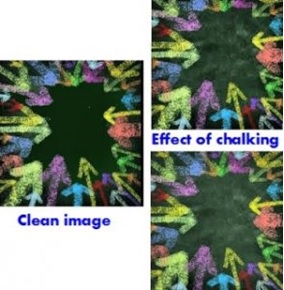
Chalking :
This is one of the defects attributed to Ink-Paper relationship. The images on the printed stocks appear to fade away or show dusty image after the sheets are printed. The deterioration on the printed image is caused by ink carrier vehicle that gets absorbs into paper too fast leaving the ink pigments in semi wet condition on the paper surface or are not getting properly absorbed into the paper thus causing improperly-dried ink getting rubbed off from the surface of the paper. This powdering defect is due to the ink that has not been properly formulated to suit the paper. The other possible reasons for this defect could be acetic paper, fountain solution too acetic (in wet offset),too soft an ink which emulsifies etc.
Doubling:
This is a Printing defect that occurs mainly due to loose blanket or paper slipping during impression process on the printing machine. Some other the reasons attributed to this defect is uneven cylinder packing,loosening of blanket during printing, grippers not holding the sheets firmly, worn out plate or blanket cylinder gears, curly paper, static charge (Static electricity) on paper, use of different blankets on the same machine etc. The image will appear blurred or shadowed.

Ghosting:
A faint image appearing on a printed sheet where it was not intended to appear. It may be termed as Ghost image. The Ghosting occurs when the printed ink excessively penetrates from the back side of the same sheet thereby disturbing the appearance of the printed image on the other side and vice versa especially where halftone images appear. One of the major reasons for this defect is use of thin paper, excessive penetration of ink into the paper due to non matching of ink with the paper, fountain solution emulsifying the ink in wet offset printing etc. Proper selection of ink with the paper stock being printed can help prevent ghosting.
Adjusting the layout itself can also help prevent of ghosting. If you have a layout that incorporates both areas of heavy ink coverage such as large, bold headlines on areas of lighter coverage on the back side, potential for ghosting on the printed sheet due to ink seepage would be higher. Therefore in such cases the layouts may be made in such a manner that the halftone images are avoided on the areas of the sheets in whose other side heavy text or image has been printed .

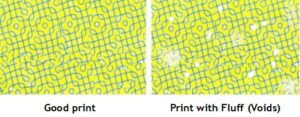
Fluff or debris:
Fluff or debris is a printing defect caused by lint and dust particles partially embedded on the paper surface getting released and struck on the surface of the plate cylinder. If the partially embedded particles are not removed from the surface of the paper, they may get released along with the inked image from the blanket cylinder surface which in turn get struck to the surface of the plate cylinder. Those particles on the plate cylinder will not accept the ink from the inking roller and cause voids on the successive prints. They are called fluff or debris or sometimes as Lint. Use of powerful anti static rod fitted suction unit will help in reducing this problem.
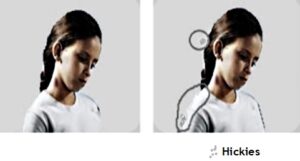
Hickeys:
This is one of the defects arising out of paper dust and improperly ground Ink. This defect prominently appears in coated stocks. Lint or dust from paper, mainly dried ink particles, or dust or other contaminants in the press room causes this defect to appear. The dust and lint from the paper gets into the ink through the ink rollers and contaminate the ink in the ink duct and subsequently gets transferred to the plate as thick particle which in turn transfers them on to the paper. The result is the appearance of blots or thick ink particle on the printed image. If the hickie- dried ink- sticks to the plate, they continue to print broken image and therefore the machine will have to be stopped and cleaned. Some times the dried thick ink particle hickie gets instantly transferred to the paper from the plate and only that particular paper will be treated as spoiled printed sheet.
Halo Effect :
A faint shadow or glow which is seen around the print especially when fine halftone image is printed may be called halo which in technical term is called halation. This is process reproduction defect arising from badly reproduced halftone negative whose exposures may not have been proper. This effect also occurs when the ink is too thin and penetrate into the paper and faintly spread the base varnish or solvent in the areas around the dots.

Misting :
Ink Misting also called flying of ink is a printing ink defect in which ink flies like mist and fall on the substance printed and other machine parts. This is common defect that occurs particularly in Offset printing presses that run at high speeds. This phenomenon of droplets of ink being thrown off or getting sprayed from the roller chain during machine run occurs sometimes in long run. The possible causes for this defect is too heavy an ink film being run on the rollers, press speed is excessive for the type of work being printed, improper ink- water balance in Offset printing machine, worn out rollers, incorrectly set rollers, the ink emulsification, too low tack of the ink etc.
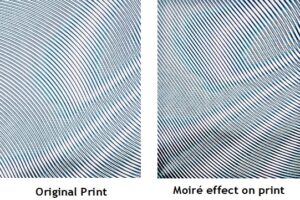
Moire effect :
Undesirable pattern showing in the multi colored print due to improper use of halftone screens during processing the films. If the screen angle has not been properly set (normally for each color separation the screen angle is rotated by 15°) during halftone processing, the dots will not fall correctly and cause distorted un sharp image.

Slurring:
This is one of the most commonly seen printing defect in Offset printing. Specially while printing halftone images, the occurrence of slurring is seen to be more. The problem could be due to
- The blanket becomes slightly loose
- The paper slips at the end of the impression
- The pressure between the plate cylinder and the blanket cylinder or between blanket cylinder with impression cylinder is heavy etc.
- If the paper is wavy, it can also cause this defect.
This is another form of doubling we can say. How will Slur look like? It will be a blurred image or a ghost image that causes the dots to enlarge due to pressure. The edges of the enlarged dots will also be not sharp.

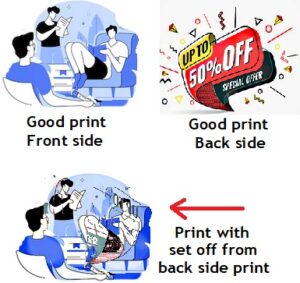
Set off :
While printing on smooth paper or coated stock of paper, it may so happen that the ink from the previously printed sheet may transfer some amount of ink from its front surface on to the back of the printed sheet which fall over it in the delivery pile. Such an undesirable ink transfer is called the Set Off. This happens due to the wet ink which failed to dry quickly. Therefore suitable ink to match the paper stock is to be selected. In the high speed machines between each printed sheets some unprinted sheet of low quality will be inserted to prevent the good paper getting spoiled. In letterpress machines Anti Set Off spray used to be sprayed with the anti set off powder on the surface of the image which will prevent ink transfer to the next sheet.
Banding defect :
This is a print defect that sometimes appear in halftone screen tints not only on the printing machines but also when the print is taken on a laser printers, image setters, or plate setters. The defect will appear on the print in the form of parallel streaks on the images.
This defect is very similar to streaking problem faced in Offset machines.The streaking will show a dark streak of image in rows at a particular point of run. This defect could be due to several reasons such as improper Cylinder bearer adjustment, worn out gear, worn out bearings on rollers or cylinders or may also be due to ink drying. If the inking form roller is not properly set with plate cylinder it can also give a bounce and cause this problem.

Streaking:
This is one of the printing defects that is commonly witnessed in Offset printing. The streaking will show a dark streak of image in rows at a particular point of run. This defect could be due to several reasons such as improper cylinder bearer adjustment, worn out gear, worn out bearings on rollers or cylinders or may also be due to ink drying. If the inking form roller is not properly set with plate cylinder it can also give a bounce and cause this problem.
Scumming :
During printing by offset process, sometimes some of the non-image areas of a plate become receptive to ink, and transfer weak tint like colour on to the paper which is called scumming. Ink adheres to non-image area of the plate during the press run and cannot be removed using a damp sponge. Sometimes the scumming may be seen only in some areas. This defect is caused by a variety of press conditions such as fountain solution that is too acidic or too alkaline, leading to desensitizing of the non image areas to become partially oil receptive (Improper PH of fountain solution). Few other causes are:
- Improper graining -coarse grain- of the plate.
- Poor plate making process adapted during plate making.
- Plate may have been partially exposed to light after coating.
- Fountain solution highly bichromated
- Glazed blanket/plate
- Excessive printing pressure
- Ink body too soft
- Improper dampening unit settings for dampening the plate
Ink drying too quickly:
Avoid the addition of drying agents to inks for general printing machines and adjust the chemicals in the fountain solution if it is Offset machine and seek the advice of Ink maker.
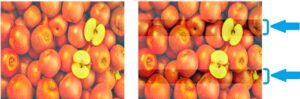
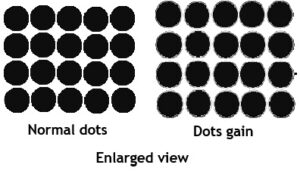
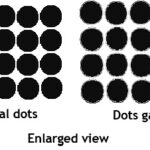
Dot Gain
Dot gain is a phenomenon that cause printed material to look darker than intended. This happens because the diameter of halftone dots increases during the prepress and printing process. Total dot gain is the difference between the dot size on the main approved file and the corresponding dot size on the printed sheets. This effect is more pronounced on newsprint than it is on coated paper.
The Mechanical dot gain- actually the printed dots becomes slightly bigger in size. This is because of higher viscosity of ink, more ink feed, more pressure between blanket and impression cylinder, deterioration of rollers, gears and drives affecting the dot size . Packing and pressure adjustments necessary to reduce this problem. Ink viscosity and flow to be adjusted. Ink roller setting need adjustment.
Optical dot gain is when dots appear larger than they actually are because there is a slight shadow around the edges of the printed dot altering the appearance of an image due to very close positioning of dots while making negatives or positives. Dots appear to be larger than they really are. The more dots in an image, the more optical dot gain appears and the image gets darker. This defect is due to wrong selection of screen and screen angle chosen while processing the films.
Emulsification:
Poor ink/water compatibility causing ink to emulsify into water due to chemicals in the fountain solution on an Offset machine. Start with minimum amounts of ink and water to obtain desired colour and adjust the fountain solution or adjust the ink qualities by contacting the ink maker.
Image Wearing during printing
Incorrect packing of plate and/or blanket or ink roller pressure on plate is high. Adjust proper packing and roller settings.
Glazing of Rollers:
Glazing of Ink rollers causing improper acceptance of ink on its surface and inking on blanket or substance. This happens due to the ink residue left in the rollers after cleaning, gum and residue chemicals picked up from the surface of the dampened plates in Offset printing, fountain solution etc. This can be prevented by proper cleaning of Inking rollers which are also de glazed periodically. Proper selection of paper matching to ink and fountain solutions are needed.

Roller Stripping:
Roller stripping is most common problem experienced in Offset Printing. The acidity of fountain solution cause the problem of roller stripping. Roller stripping means non acceptance of the ink on the surface of the inking rollers or the roller becomes ink repellent. The ink rollers which are in simultaneous contact with the plate along with the dampening rollers, pick up the traces of the acetic water from the plate and thus their surface slowly gets glazed by the action of acid thereby emulsifying the ink too .
The acidity cause the rollers to become blind or too glazed not to retain the ink on its surface and start repelling the ink. The entire roller surface does not become blind and only when the water droplets stayed on the rollers during running, wherever the droplets were there the rubbing action in those areas cause the blindness and therefore they are found to be in patches. Decreasing the strength or the flow of the fountain solution may help alleviate the problem.

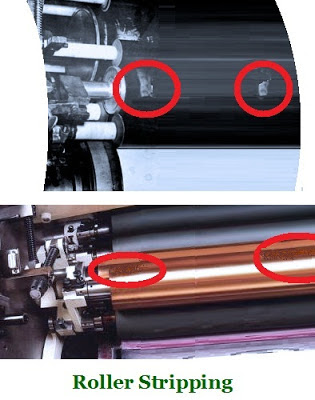
The rollers also gets glazed due to continuous running over several thousand runs.The Copper based rollers have less tendency to roller stripping compared to Steel rollers. In order to overcome the problem, the rollers could be washed thoroughly with a strong metal glaze remover which is available in the market or the other alternative would be to desensitize the rollers with suitable solutions available for the said purpose.
One important question may be arise. Is it true that only the metal rollers become blind (Glazed) ? What about the rubber rollers ? Not only the metal rollers, but also the rubber rollers refuse to accept the ink at some places at some stage, which is a sort of Roller Stripping. Whenever the ink on the rollers dried on the surface of the rollers, or due to the constant rubbing action of the pigment particles of the ink, the roller surface become polished, then those areas rub off the ink without holding them (ink slipping). In such a case the roller will have to be removed and re rubberized.











Recent Comments