
Alphabet -P /2



9. Parchment: This refers to a variety of paper. There are two varieties of Parchment papers in use. One is used in the printing industry for printing special print material such as Awards, Certificates, Business cards, Menus in the restaurants’, Poetry books, and several such rare and unique material. The print design on them may be of calligraphy and ornate script fonts in nature to give antique look to the print material. The Parchment paper used for such work will be thick, tough and design embedded as most of them are hand made papers.
Another variety of silicone Parchment paper is also in use for packing baked products, cooking or food packaging as they withstand high temperatures, and are grease and moisture resistant. The said quality Parchment paper is coated with a nonstick material, typically silicone, to give them nonstick properties.
Earlier parchment papers used in 15th century were made out of the skin of certain animals like calf, goat, or sheep. Subsequently instead of animal skin, plant based parchment papers came into being. The plant made Parchment Paper is made from fir trees or plants such as cotton or flax or alpha cellulose, known as water leaf, which contains no sizing or filling materials. The pulp is treated with sulfuric acid converting a part of the cellulose into a gelatin-like colloidal. When the sulfuric acid is washed off, the colloidal film hardens on the paper. The strength of the paper thus gets increased and will not disintegrate even when fully wet.
The finer variety of Parchment paper is called Vellum. Vellum is Latin word meaning made from calf, and a thin skin material thus prepared was used for writing or printing single pages, scrolls, or rare manuscripts books, Bible etc in medieval period. Since the Parchment paper made with animal skins were not weatherproof, the books printed on with parchment pages were bound with strong wooden boards as cover and kept firmly clamped by metal caps to keep the pages remain flat and to ensure that they do not get distorted due to changes in the humidity. Now similar paper is manufactured treating the cellulose fibers with sulfuric acid to make them weather proof. Because the paper is thicker and has a non uniform textured surface, printing will have to be done with care to achieve good results.
10. Panchromatic (Films): The word Panchromatic refers to films that are sensitive to all wavelengths of the spectrum. Two types of films are available, both Panchromatic in nature. They are Panchromatic films meant for photographic purposes and the other Panchromatic films for Graphic arts process. While both are important in the field of printing, the Graphic arts film is more important for Printing presses. The Panchromatic films are used for preparing color separated negatives and positives to make printing plates to reproduce the colored original in print form. The colour separated negatives or positives are prepared using different colour filters to control the imaging on the Panchromatic film.
Unlike Orthochromatic films which are sensitive to all colours except Red, the Panchromatic Film is sensitive to all colors including Red. In the case of Graphic arts panchromatic films, one can find the recorded images represented in greys and blacks instead of in color where as in the Photographic Panchromatic films, the recorded images will show actual colors after developing. In Graphic arts Panchromatic films, the densities of gray can range from dense black to lightest greys as they depend upon the brightness of the the color in the original and the color sensitivity of the film used. Several Photographic film makers like Agfa, Gevaert, Fuji, Ilford, Kodak, DuPont, Fomapan and some more firms produce the films in sheet form and as Glass plate films for use in Graphic arts industry.

11. Paste Drier: The inks dry generally by three major processes such as Oxidation, Polymerization and Penetration. There are two types of driers available for adding with the ink to facilitate drying of the inks on the printed stocks. They are Liquid drier and Paste drier. Amongst the two, a compound in the form of a paste which is added with the inks to accelerate the drying process is called Paste Drier. The Paste drier contains some metallic portions such as Cobalt, Manganese, or Lead along with some liquid form of resin or oil. The Paste drier act as catalyst to increase the speed of drying along with Oxidation and Polymerization process. If excessive Paste drier is added, that may cause some of the printing problems. Therefore care may have to be taken to add suitable proportion of the driers in consultation with the ink maker.
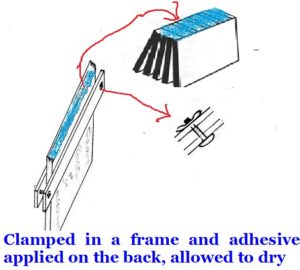
12. Perfect Bind or perfect binding: A technique of binding the books with some strong adhesive like glue, Fevicol etc and to fix the outer cover on them. The edges of the books will not be stitched or threaded, instead they will be tightly held and glued or some strong adhesives applied on their back in such a manner that the glue or the adhesive intrude slightly into the book edges and hold them firmly without allowing the loose leaves to fall. Perfect binding is solely adhesive based binding.









Recent Comments