
The evolution of plates for printing

Initially when various printing processes emerged, the plates for printing by Letterpress, Offset and other printing processes were made on different materials such as Lithographic stone for Lithographic printing (direct Offset) and metal plates like Zinc or Aluminium for other processes including Offset. In course of time, besides lithographic lime stones, several other metals like Zinc, Aluminium, Brass, Magnesium and Copper were also used since adjusting the quality of the images formed over the plates for quality printing were easier to perform with certain acid solutions on them.
The heavy weight of the metals and Lithographic Lime stone caused several working problems in handling and processing of the plates and therefore alternate materials, lighter in weight and easier to process were thought of and led to the invention of several plates such as Pre sensitized thin plates, Paper based metal coated material and Photo Polymer plates whose inventions not only reduced the weight of the Plates fitted on the printing machines, but also considerably shortened the processing time involved.
In respect of printing plates meant for Flexo printing process, major development has taken place. The Flexo Printing which is similar to Letterpress is conventionally performed with relief plates prepared on soft Rubber or plastic based material called rubber stereos. When Flexo printing was introduced for printing on packing materials, the printing plates used were engraved Rubber stereos. Subsequent development saw Photo polymer plates replacing the conventional Rubber Stereos for the same print process. The Photo Polymer technology further developed with the release of newer generation Liquid Photo polymer which has been seen as an excellent replacement for Polymer supplied in sheets because the cost of making a plate from Liquid Polymer was considered to be substantially lower than the conventional sheet of polymer.

The Printing plates for the Letterpress process is almost similar to the Flexo process except that the plates required for the Letterpress printing is not processed on rubber based material but prepared on thick metal sheets like Zinc, Aluminium, Magnesium and Photo Polymer plates. The printing plates were actually called Blocks and not plates because they were smaller in size, mounted on a wooden block support before uploading on the machine. Moreover the blocks were meant only for printing the illustrations and images part. The blocks containing illustrations were clubbed with the composed metal types and locked in the forme for printing. The relief areas on the blocks accepted the inks directly from the inking rollers without need for pre wiping, pre spraying or pre scrubbing the plate with any other fluid or water to prevent non image areas accepting the ink.
The next development was moulded metal plates for printing on rotary machines since the loose type metals, composed by hand or on hot metal type casting machines that formed the text material and the blocks could not be mounted on curved surface of the cylinder. The combined text material and image holding blocks were converted into curved metal relief plates by a process called moulding process. The final material from the composed types and blocks for printing were first impressed on rolled or flonged stereo mats in the finalized Laid out format. Papier machie mixture was used as flonged stereo mats for making a mould and curved to required shape before the metal plate required for uploading on the machine for printing was cast with molten material consisting of antimony, lead and aluminium alloy. The mould cast plates thus prepared were mounted on to the cylinder for printing. This process was also cumbersome, time consuming and the curved moulded plates heavy to handle besides causing lots of technical problems in use.
Beyond this, not much development was done for innovation of newer type of plates (blocks) other than Photo Polymer which reduced the processing time, weighed less and also cost lesser than the metal plates. To speed up the process of making plates (blocks) which were initially made of metals like Zinc, Aluminium, Copper, Magnesium and Brass and the moulded plates with few metal combinations, the plates made out of Photo Polymer plates began to be used.
Though direct on metal processing mechanical engraving machines like Vario Kleschograph too lent some support for speedier production of plates for Letterpress process no other material has been developed to replace the conventional metal plates like Zinc, Aluminium and Magnesium. The Photo Polymer plates helped in combining the text matter and the illustrations in easy manner to prepare any size plates with relief images in quick time eliminating many cumbersome intermediary processes.
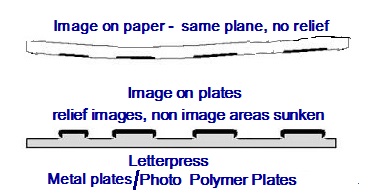
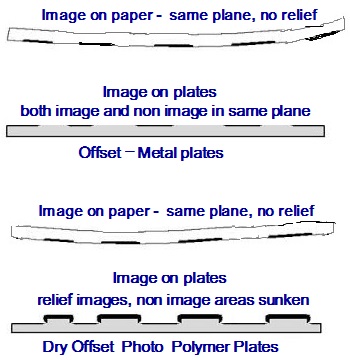
However in respect of Offset process of printing which is based on Oil-water repellent theory, the invention of newer plates were gradually taking place in some part of the world or the other to replace the intervention of dampening the plates which was inherent with some technical problems. In wet Offset printing process unless perfect water- ink balance is maintained, the required print quality can not be derived. Offset printing process consists of plates where in the image areas and non image areas lay in the same plane – the images to print are oil-receptive (oleophilic) and the non image areas which are not to print remain water-receptive (hydrophilic).
As the technology progressed, use of Lithographic lime stone for printing by Litho printing process was replaced with repeatedly usable metallic plates like Zinc and Aluminium as the metallic plates could be subjected to surface grinding to erase the temporarily adhering previous images for reuse of the plate again and again by using certain material like fine sand stone and glass balls combined with water followed by certain acid treatments. The process was cumbersome, needed not only more space to accommodate the machineries and equipments, but also more processing time was required. Most importantly the quality of the image and the ink absorbency depended on the surface angle of the pits created after the plate had been grained thereby necessitating a perfect graining process. The surface angle of the pits depended on the process of graining and materials used in the graining process. Actually all these combined problems led to the necessity of invention of some material to be used as printing plates and thus led to the invention of the Polymer plates.
Photo Polymer plate was invented to process the plates in the shortest possible time at lower cost besides eliminating entire pre processing time. Those plates can not be reused also. There was another reason to glee over introduction of Photo Polymer plates which did not require dampening the plate during print process. The printing process with Photo Polymer plates which had the image areas in relief and needed non engagement of dampening system was called Dry Offset Printing which in strict sense was the combination of Letterpress and Offset Printing process.
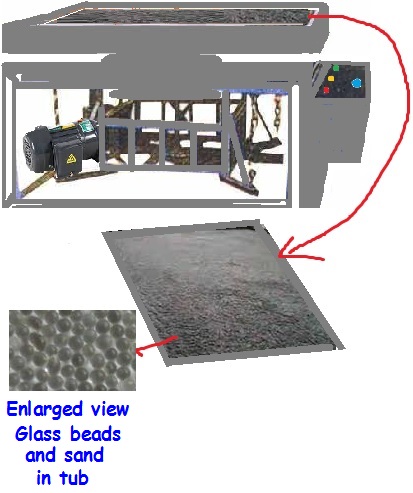
Before a metal plate like Zinc or Aluminium could be processed for Offset printing, its surface needed to be subjected to certain mechanical and chemical action to turn it to hold the image areas on its surface for printing on the machines. Since the basic structure of the metallic aluminium in sheet form is very smooth, when water is applied on the smooth surface, it had the tendency to bleed over the entire surface. Since the Offset printing plate need only a layer of water to stay on the non image areas and ink to remain adhered on the image areas of printing without either of them bleed into the others thus disturbing each of their functions, the surface needed to be roughened to have micro fine pits which can be created by evenly rubbing the overall surface with the use of balls and fine sand which is called graining process.
Conventional plate graining machine grinds the plate inside a tub in heave action (moving front and back) with glass balls and fine sand mixed with water put over the plate.
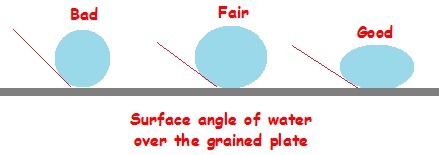
In short the graining process is nothing but roughening of the plate surface to remove previous images and to create fresh micro pits called grains on the same surface to enable the plates reusable several times by erasing the previous images. Such an action – graining to create micro pits on surface – provides better latitude for technical requirement such as ink/water balance on press, cause less trouble with dirt and hickeys, and less tendency for dot slur which mar the quality of image on print.
Emergence of Anodized Aluminium and Paper plates :
Prior to the introduction of Photo Polymer plates, the outdated technology of mechanical graining process got converted into electrolytic graining called anodizing process by which thin tin sheet was electrolytically deposited with a thin layer of rough surfaced aluminium to use as printing plate as against the conventional Zinc and Aluminium plates. When anodized metal plate was found to function as good as grained plate, the annodization process replaced the mechanical plate graining process thus paving way for the introduction of Anodized aluminium plates for use as printing plates for small Offset printers on small to medium size machines. When anodized aluminium plate was introduced, simultaneously one more intermediary plate with Paper base was also introduced for use on small Offset machines.
What is Paper plate? :
A special paper based metal sprayed printing plate with laminated back, meant for use on small Offset Printing machines like Romayor, Rota print, Swift, and Adast Offset machines was introduced prior to the introduction of Anodized Aluminium plates. Their usage is gradually diminishing due to the electronic and digital printing. Special Paper plates, also called Rotamasta Paper were similar to thin anodized aluminium plates and supplied with special non stretchable laminated paper base coated with some kind of material similar to the properties of Zinc or Aluminium plates. Even though their use is diminishing, still in some parts of the world small Offset printers continue to use them. Being flexible material the print matter could be photo copied directly on Xerox machines or typed directly on a typewriter machine, but using special typewriter carbon ribbon instead of conventional typewriter ribbons. Even direct writing with special oil receptive ink was possible for adding sketches or drawings along with the text material typed or copied on the plate. Once the image are formed as above, the plates are treated with a special solution supplied along with the paper plates that convert the surface properties of the plates to that of Offset printing plates – water resistant on image areas, and ink resistant on non image areas. The Paper plates were meant for short run copies on small offset presses and were made available to the maximum size of A3. Though these plates were found easier and quicker to produce and handle, certain limitations as experienced in the technical aspects including registering the images led to the development of the production of thin anodized aluminium plates.
What is annodization and a anodized plate?:
In the first instance after thick Aluminium plates, reusable several times by graining process emerged as alternative to the conventional Zinc plates which was the only metallic plate used initially, the emergence of Anodized Aluminium plates further proved to be boon in this sphere. In fact only the Anodized Aluminium plates opened up the avenue for the development of Pre sensitized plates in early 80s since most of the Pre sensitized plates were initially supplied on Anodized Aluminium plates only.
Anodization is a process by which extremely hard aluminium oxide is electrolytically deposited on the surface of a grained aluminium or tin sheet which further converts the plate surface into corrosion resistance
aluminium. The anodized layer has several micro pores or micro pits, the pattern of which could be compared to a honeycomb. Thus the Anodized Aluminium plate which undergo the annodization process turns the metal surface into twin quality material such as water-receptive and oil receptive one. The anodized plates behave similar to conventional aluminium plates and are economical for small offset presses, easy to use and work well on the press. These plates were improvised version of Paper based plates. Anodized plates are also reusable by recycling them for a few times by performing chemical graining (removing the old image by etching process) instead of subjecting them to mechanical graining. The process of erasing and re imaging even for few times provided not only economic advantages but also environmental benefit as well.What is a Pre sensitized plate? :
However whether the printing plates required for printing were of Zinc or Aluminium, they could be made ready for printing only by two or three processes called Albumen or Glue plate making processes or Deep Etch process of plate making whose sensitizer and processing solutions were entirely different in nature. Conventionally the metallic plates like Zinc or Aluminium required for printing used to be processed by first coating them with some light sensitive solution, allow them to dry and then exposing the coated plates through negatives or positives to transfer the print image over them. The exposed plate underwent certain chemical treatments to get the print image firmly stay over the surface of the plate for further printing. The entire process involved several steps of processing which consumed much time.
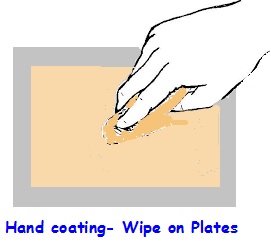
As said earlier the development of Anodized plates which were primarily meant for short-run copies was instrumental in the development of plates’ called Wipe on Plates and ‘Pre sensitized plates’ which eliminated several intermediate processes. While the Wipe on plates were meant for making plates using Negative, the Pre Sensitized plates were made available to work both with Negative and Positives. While the Wipe on Plates were to be hand coated with special sensitizer solution, the Pre Sensitized plates were ready to use (directly exposable with negative or positive)
pre sensitizer coated plates which needed no hand coating of sensitizer.What is Wipe on Plate ? :
Before the introduction of the Pre sensitizer coated plates Wipe on plates were introduced processing printing plates in the quickest possible time eliminating certain pre exposure equipments. Since a ready to use sensitizer solution which was made available was swiped (wiped) on the anodized aluminium plate by hand with a plain cotton wool or smooth soft cloth dampened with the sensitizer solution such processed plates were called Wipe on Plates. The coating could not be expected to be uniform, but the hand coated plate dried in few minutes after swiping the plate with the sensitizer solution, allowed it to dry, exposed with negative or positive and then washed with water and a special solution supplied along with ready to use sensitizer to make ready the plate for printing. The Wipe on plates were easy and quick to process, but the reproduction of the halftone images were not as good as normal processed plates because of non uniform coating by hand. The plates processed as above, called Wipe on Plates helped the small printers to quickly prepare plates for short run copies at short intervals. Such type of plates were not made available for printing by Letterpress, Gravure or by Intaglio and only for Offset printing plates they were available.
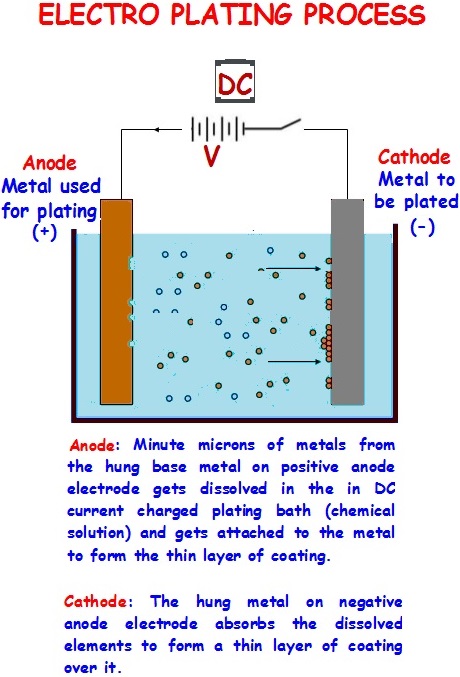
With the passage of time in order to produce plates which can give several thousand copies without quality loss, use of multi layer metallic plates made ready by electrolytic process were introduced for Offset printing. Initially they too were negative and positive working plates, but could not be made available in the form of Pre sensitized plates. The electroplating process based plates had to undergo various steps. The concept of use of multi metal plates gained momentum and two types of multi metal plates were in use. One was called Bi metal plate meaning combination of two metals, while the other one was called Tri metal plates- a combination of three metals.
What is Bi metal plate?
Generally the Bi metal plates consists of either Aluminium or Steel base on which Copper was coated in the image areas to hold the images. The Aluminium or Steel based plates used to be coated with special sensitizer solution, exposed through negative or positive as the case may be, and treated with chemicals to ensure that the image areas bare the base metal Aluminium or Steel. In the second step a layer of copper used to be deposited on those open areas of Aluminium or Steel. The Copper has the oil absorbing ability (oleophilic) while the base plate Aluminium or Steel is more of water receptive (hydrophilic). Finally when the plate is washed it was left with the image areas in copper and the non image areas showing Aluminium or Steel metal. The finished plate, chemically treated was protected to prevent their surface getting rusted till the same is fitted on the machine for printing.
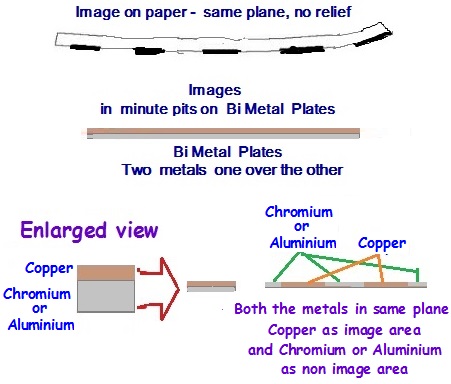
Similarly the other type of Bi metal plate consists of coating Chromium over a base metal plate like Copper or Brass and then processed to etch away the Chromium coating from the image areas exposing either the Copper or Brass base which will form the image areas. The Brass or Copper will accept the ink as they have oleophilic properties while the Chromium will act as water absorbing hydrophilic metal. However the Bi metal plates could only be used for printing by Offset process and for long run of single job due to economics on cost.
What is Tri metal plate?
One other plate meant for Offset printing is called Tri metal plates which is a plate made with three metal combination. The base metal used to be steel or aluminium over which a thin layer of copper coating used to be given. Over the thin layer of copper, again a thin layer of chromium coating used to be given. By subjecting the plates to processing like coating with sensitizer solution, exposing through negatives or positives followed by special chemical treatment the chromium is etched away from the image areas, showing the copper layer below on the image areas. The chromium which has the properties of water receptive (hydrophilic) remains as the non-image areas of the plate while the Copper which has oil (ink) absorbing ability (oleophilic) remains as the image areas over the plate. Both the coatings are held firmly over over the surface of steel or aluminium base metal. This again is a slightly complicated, time consuming process and the cost of producing the plate is also much higher.
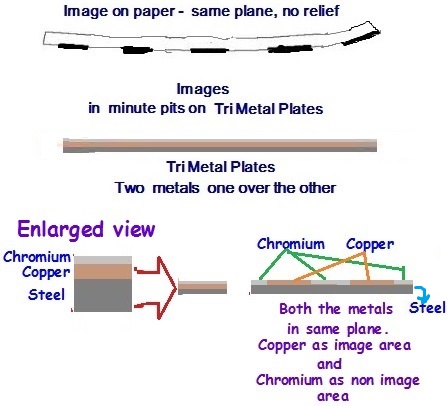
There were advantages as well as disadvantage in the use of both the Bi and Tri metal plates. They undoubtedly gave very long runs compared to all other plates fitted on the machines, but very expensive and time consuming process is involved in producing such plates. Therefore only the printers whose print orders used to be millions of copies of the same print were beneficiaries, while the small and medium printers could not afford to have the Bi and Tri metal plates. Moreover if for some reason the plate got damaged during run, the cost benefit will be lost. However the one most important aspect lay in the use of Bi and Tri-metal plates were the non requirement of the graining process as they worked on chemical process involving the principle of electroplating .
While the production of plates by this process waned away with the emergence of Photo polymer plates, the same principle of Bi and Tri metal combination re emerged in a different form paving the way for the production of plates for Intaglio printing process.
Intaglio printing Plates:
The Bi and Tri metal technique of plate making opened up the avenue for making plates for the Intaglio process of printing. The process involves four stages of processing- all based on electroplating technique and found to be not only cumbersome, time consuming but also needed several equipments and machineries besides sufficient space. The processing of this type of plate involved something like first preparation of moulded plastic (images in relief) from master steel engraved die (images in depth) which hold the final image to be printed. Several moulded plastic (images in relief) moulds taken out of the master plate is laid out to final format of plate based on the print layout; from the said laid out mould, multiple up copper plate is (images in depth) produced by electroplating process, from which a Nickel plate (images in relief) is produced again by electroplating process, from which the plates needed for the printing machines are produced as chromium plates (images in depth) by electroplating process. Each of the Chromium plate has to undertake few tons of pressure over it during the process of image transfer from plate to paper, still retaining same size and shape. Since ready to use plates can not undertake such transfer process invention of machines like Computer to direct Plates became necessary.

Emergence of Photo Polymer plates:
One of the plates used in Printing is the specially pre sensitized Photo Polymer printing plates, meant for Dry Offset or Letterpress printing and which can be taken out from the box and directly exposed with negative or positive and simply washed with water or alcohol to get the relief image. No special solution is necessary to process the plates. The light passing through the negative or positive polymerizes the image areas and harden them to show in relief as the image areas which will remain insoluble in water or alcohol. They are then dried and preserved for printing.
Photo polymer is a synthetic material which is made available in sheet form and is sensitive to light. The photo polymer or light-activated resin changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The Polymer has the tendency to get hardened when exposed to ultraviolet light and the extent of hardness is related to the amount of UV light it receives.
The Photo Polymer plate consists of a layer of thick photo polymer material coated over thin sheet of metals like aluminium or steel. Photo polymer plate which is photosensitive material is exposed through the negative under UV light to form the image areas. After exposure when the plate is washed out with water or alcohol the hardened areas remain insoluble in water or alcohol and the unexposed polymer gets washed away either in water or in alcohol. The hardened areas remain the image area in relief form since the unexposed areas surrounding it gets washed away.
One most important aspect of the Polymer plate is that they are ready to use plates supplied in the form of pre coated plates, i.e. sensitizer solution combined Polymer, Nylon or even Acrylic material which need no processing in the conventional manner, thereby eliminating certain processes before exposing the plates through Negative or Positive films. In strict sense they could be termed an extension of Pre sensitized metal plates, but relied on most advanced graphic arts technology.
The first synthetic based photo polymer plates for imaging applications were reportedly invented in America sometime in the year 1952 aimed at processing of photo engraving and Offset plates. As these transitions in the process of making plates for the Offset and Letterpress were going on till late 1990, the invention of Polymer plates silently emerged sometime from the year 1955 itself or a little later when Time Inc, a Multinational mass media corporation established in US (in 1922) which owns and publishes over 100 magazine brands, most notably its flagship magazine called Time came out with a Nylon based Polymer plate meant for Letterpress process. It was called Tylon Plates. The offshoot of Tylon plate was development of Dycril and Nylon based Nyloprint printing plates. Close on the heel came developments of Photopolymer plates from DuPont and BASF.
In the year 1960 DuPont came out with Polymer plate in the name of Dycril plates which was acrylic based while in 1968 BASF came out with similar plate in the name Nyloprint which was nylon based. However all those plates were only usable in Letter press and Offset process besides Flexo printing process. Both the plates had to be washed (developed) with alcohol solution for reproduction of image on the plates for subsequent printing.
In further development much later BASF came out with water washable plates replacing alcohol wash. Closely following these developments one other American conglomerate namely ‘E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company’, commonly referred to as DuPont, initially established in the year 1802 as a gunpowder mill diversified its activities to develop Polymer products such as Vespel, neoprene, nylon, Teflon, Mylar, Tyvek etc. Their initial product Photo polymer plate was named Dycril printing plate. In mid of 1970 some of the Japanese firms like Toray industries, Printlight industries and Tokyo Ohka Kogyo too entered into the field of production of Photo Polymer printing plates.
Some of the major firms who produce Polymer based printing and Photo engraving plates include the following group of companies:
- M/s Hercules, U.S
- M/s Grace, U.S
- M/s DuPont, U.S
- M/s Polyfibron, U.S
- M/s MacDermid, U.S
- M/s Kodak Polychrome subsidiary of Eastman Kodak Co, U.S
- M/s Agfa, Belgium
- M/s Imation, U.S
- M/s Chemence, U.S
- M/s Southern Litho, U.S
- Solarplate, New York
- M/s Lastra, Germany
- M/s XSYS Systems, U.S
- M/s Flint Group, U.S
- Asahi, Japan
- Toyobo, Japan









Recent Comments