
Guide to printing students -18

Guide to printing students
-Few objective Questions and answers-

Written by : N.R. Jayaraman
Pre note:-
The articles are meant to help the students gain knowledge and effectively compete in the interviews and nothing else. Please note that these are not to be published by anyone for commercial purpose without the written permission from the author since the theme and illustrative examples have been compiled exclusively by the author for the benefit of the student community. THIS WILL BE PERIODICALLY PUBLISHED.
87) What is Aquatint process? Who invented it ?
Like Mezzotint, this is also one of the processes under the umbrella of Intaglio process in which the image to be printed are created on the metal plate and various densities of tonal values are derived by etching specific areas for longer or shorter time to deepen the pits which carry ink after covering the areas not to be modified with Rosin powder. Gradations of tone are achieved by varying the length of time in the acid bath-longer periods produce more deeply-bitten rings, which print darker areas of tone, while lesser periods of etching produce pits to carry lesser ink.
The process of creating the image on a zinc or copper plate involves the use of Rosins and Acid and since the prints taken from those plates often resemble watercolor paintings, it is called Aquatint process, Aqua meaning water. However the non-tonal work (Halftone) carrying only lines and dots or other patterns are also produced by this process. Normally the plate required for printing is prepared on either a Zinc or Copper plate. Once the printable image is created on a plate, the plate will be inked by suitable inking process or technique and passed through a printing press after keeping a sheet of paper on top of the plate to transfer the ink on to the paper.

Aquatint was reportedly invented by one artist named Mr Jan van de Velde in Amsterdam in the year 16th century while it was widely practice in England in the 17th and 18th century. Aquatint process was popular in England, France, Spain and some other European countries during 17th century.
The brief of the process is this. The illustration to be reproduced is traced down on the plate, the plate surface dusted with fine rosin powder, plate heated to melt rosin which may appear as minute grainy layer showing tiny channels of space in between the grains. The plate is then dipped in the acid which eats the plate through the open channels where thinnest layer remained. While repeating the etching in other areas, the already etched areas are covered with some ink and allowed to harden before subjecting the plate to repeated etching. The rosin is acid resistant and adhere to the plate by controlled heating. Thus the tonal variation is controlled by the level of etching.
88) What is Lithography and Lithographic process and who invented them?
Lithography is a Greek word meaning writing on stone. ‘Litho’ means stone and ‘Graphy’ means to write. It is a planographic process in which both the image areas to be printed and the non-image areas rest on the same plane or surface. It works on the principle that the Ink and Water repel each other. The Lime stone has the properties of holding both greasy ink and water over its surface thus allowing any oily ink to stick to the image areas while non image areas accept resisting oily ink. The prints are taken after applying ink to the grease-treated image on the flat printing surface (which is a stone) and non-image areas moistened with water.
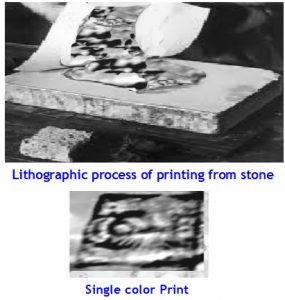
In the earlier days the Offset printing was known as Lithography because instead of metal plates, special natural lime polished stone was used as printing plates. The process in brief is this. The images used to be drawn, text written by hand with certain semi fluid oil based inks or composed matters transferred on to the stone by transfer paper process. The transfer papers used to be coated with some gelatin like substance, processed, and then the prints from the composed matters taken on them, from which the images were transferred on to the stone. After treating the images on the stone with gum and other dilute chemicals to enhance the natural properties of the Limestone, the stone is made ready for printing. The ink is applied over the inked image through an inked roller after wetting the surface of the stone with a wet sponge. The paper on which the prints are to be taken is placed over the inked stone and pressed evenly through a blind roller or other pressure rollers to transfer the inked image from the stone on to the paper. This process of taking prints from a stone is known as Lithographic process of printing. In this process only one colour printing per image embedded on the stone was possible. This process set the basic concept for development of Wet Offset Printing using metal plates replacing stone.
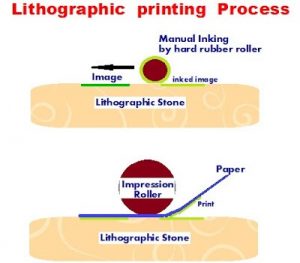
Lithography was first invented in 1798 by a German named Aloys Senefelder in Germany. He initially an artist who practiced the art of copper plate engraving process. His invention- Lithographic process- when revealed in the year 1818, attracted the attention of several artists who began to adapt it for reproducing the illustrations and drawings into print. In late 18th century it was widely practiced in Europe, especially in UK and machines were developed to take prints from a smoothed limestone on which the images to be printed were drawn or transferred through other means.
88) What is Chromo Lithographic process and who invented them?
Chromo is Greek means colour. Chromolithography is extension of Lithographic printing. While initially one colour printing was done by Lithographic process of printing emerged, by the use of more no of stones incorporated with the same image, each stone carrying only the split portions of the image which needed to be printed in specific colour multi colored images were printed. Before preparing as many colours needed, as many stones were also made ready by tracing only part of the image on each of the stone. Thus as many stones as required for printing specific colours will be prepared for taking print from them. Same sheet of paper will pass through the printing press as many times as there are colours in the final print carefully registering the paper using register marks. Even though high quality reproduction was made possible by this process which was expensive and slow, it was generally applied for printing greetings cards, posters, and small labels and picture post cards etc. It flourished during Victorian Era.
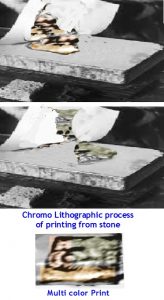
It is claimed that the art of Chromolithography was invented by Godefroy Engelmann of Mulhouse in France in the year 1837 as a patent has been officially allotted to him on that year even though it was believed to have been practiced by many artists even earlier to the award of the patent, but this could not be confirmed.










Recent Comments