
Counterfeit Currency Reports and FIU
Counterfeit Currency Reports
and
Financial Intelligence Unit
and
Financial Intelligence Unit
(Written by N.R. Jayaraman)

There is growing concern on the issue of fake money in circulation not only in India, but also around the world. In spite of concentrated efforts made internationally to eradicate the menace of forged currencies, the result has not been fruitful in totally eliminating the menace. The only little consolation the authorities can have is that the measures taken by the Govt institutions and agencies have been able to make the task of counterfeiting more and more difficult unlike in the past when the fake currencies could be easily circulated with the help of colour copiers. Beyond making the task of forgery more and more difficult, nothing could be done to eliminate the menace as each passing day the menace is emerging in different manner, some of which are linked with terrorist sponsored states. Setting aside the primitive printing methods, criminals involved in the racket of fake currency use sophisticated gadgets to manufacture fake notes which conform to almost all security parameters.
In so far as India is concerned the counterfeit currencies flowing from across the border to aid terrorism, destroy economy and as regularly practiced by hoarders and mafia empires is alarming and cause of concern to the govt.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) which is the central agency for the printing and circulation of the Currencies for the Nation has been adopting multi prolonged approach like strengthening the security features in the currencies with worldwide acceptable features as well as various other steps as part of exercise in robust currency management. In this direction RBI is also planning to introduce plastic notes to reduce forgery and thwart other illegal activities related to circulation of fake currency .
In one of the advisories, the Govt through RBI reportedly conveyed that all the banks in the country, whether private, public or foreign and other similar financial intermediaries are mandated under anti-money laundering laws and other rules related to national security, to detect and send instances connected to and Counterfeit Currency Reports (shortly called CCR ) to the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) which is the premier snoop gathering agency set up in 2004 for gathering and analyzing such instances in the country and the said agency was functioning under the control of the Finance Ministry. RBI has specified to the banking industry, the reporting formats and electronic data structure for submitting CCR vide a circular in the year 2008.
Counterfeit Currency Reports is defined as a suspicious alert report that includes details of even a single instance of counterfeit currency as detected by any bank. Upon receipt of the reports, the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) after due analysis sends the Counterfeit Currency Reports to various other security and intelligence agencies in states and central units for appropriate action at their end.
To address the multidimensional aspects of the fake Indian currency note menace, several probe agencies are already working in tandem to thwart the illegal activities related to fake notes circulation. However in ground level since there were multiple agencies probing the cases of fake currency, their inputs varied from case to case and it became necessary to probe such instances on a case to case basis which resulted in projecting confused picture in identifying the motives or the agencies involved. Therefore the Govt desired that if a centralized nodal agency could study all the cases sent to it, it can then analyze all aspects including identifying and understanding the trend of fake Indian currency notes in the country.
The need for continuous and deeper study on fake notes was felt during one of the meetings of the Economic Intelligence Council, an apex body on financial crimes, whose deliberations according to the observers culminated into the above action plan finally resulting in the emergence of FIU.

The Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), an independent body reporting directly to the Economic Intelligence Council (EIC) headed by the Finance Minister was set up sometime in 2004 as the central national agency responsible for receiving, processing, analyzing and disseminating information relating to suspect financial transactions. FIU interact with Enforcement Directorate, Ministry of External Affairs, Intelligence Bureau, National Security Council and the Research and Analysis wing for effective functioning in achieving set targets under Prevention of Money-laundering Act, 2002, one of the target being to receive, analyze and disseminate information on fake circulation of notes for providing useful information to law enforcing agencies for further action to curb the menace. In short FIU is interface between financial sector and enforcement agencies.
The Prevention of Money-laundering Act, 2002, and rule thereunder require every banking company, financial institution and intermediary, to furnish to FIU information relating to all cash transactions where forged or counterfeit currency notes or bank notes have been used as genuine or where any forgery of a valuable security or a document has taken place facilitating the transactions.
How seriously was the advisory responded by the Banking industry? It is learnt that in compliance to this directive, initially the response from the public sector banks was lukewarm and was a cause of concern to the Govt probe agencies as the public sector banks held the largest customer base in the banking industry and large money transactions were involved and surely here and there the entry of fake notes in transacted currencies could not be ruled out.
In view of the lukewarm response received from the public banks, the financial enforcement agencies in coordination with the Indian Banks’ Association devised measures like pre warning signals and training programmes to quickly detect such currencies received by the public banks in order to ensure hundred per cent compliance in reporting this to the Financial Intelligence Unit.
On the other hand the private banks reportedly played effective role by detecting maximum number of Counterfeit Currency Reports over the years and reporting to Financial Intelligence Unit. Even then in the same corresponding years of reports sent by the private banks, the contribution of public sector banks were quite low as may be seen from the figures given in the following table.
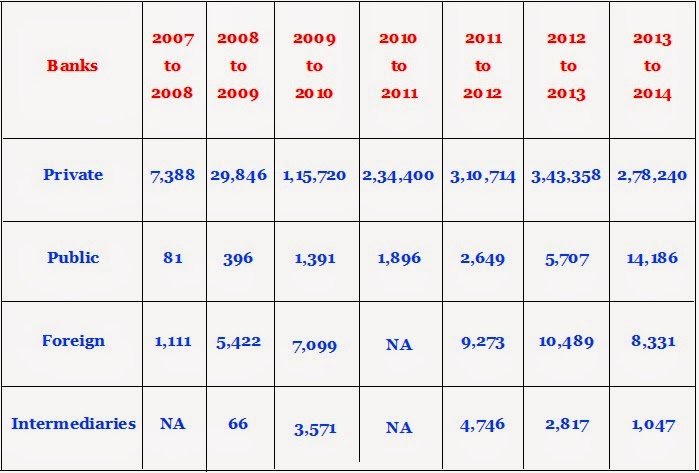

(Data in table – Courtesy: http://fiuindia.gov.in/publications-report.htm )
In the last few years due to continuous and concentrated efforts of the Govt agencies, particularly FIU, there has been an increase in seizure of fake currency notes in the country due to the ever increasing reports received by FIU. As per the Annual report of FIU, during 2009-10 period the no of Counterfeit Currency Reports received by FIU shot up by 250 % i.e 1,27,781 reports compared to only 35,730 reports received during 2008-09 period. Efforts were made to ensure that even small incidents involving one or two fake notes were not left out from reporting.
The menace of fake note circulation is mainly on account of the criminal network from several neighboring countries that are pumping fake Indian currency notes into different parts of the country to disturb peace and destabilize the nation says the concerned officials.

The Press Information Bureau press release dated 6th December 2014, notified the following information :
Quote:
……To address the multidimensional aspects of the FICN (Fake Indian Currency Notes) menace, several agencies such as the RBI, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Home Affairs, Security and Intelligence Agencies of the Centre and States, Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) etc., are working in tandem, to thwart the illegal activities related to FICNs. The work of these agencies is periodically reviewed by a nodal group (FCORD) set up for this purpose. FCORD (Fake Indian Currency Notes Coordination Cell) coordinates/shares all available information/intelligence and analysis on circulation/smuggling of FICN in the world. At the functional level, the CBI has been declared as the nodal agency for coordination with the Sates and the Directorate General of Revenue Intelligence has been nominated as the Lead Intelligence Agency for the purpose. National Investigation Agency (NIA) has been empowered to investigate and prosecute such offenses to deal with this menace. The government has also constituted a Terror Funding and Fake Currency Cell (TFFC) in NIA in 2010 to focus on investigation of Terror Funding and Fake Currency Cases. Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has also strengthened the mechanism for detection of counterfeit notes by the banks. (Courtesy- Source: http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease/)
Unquote
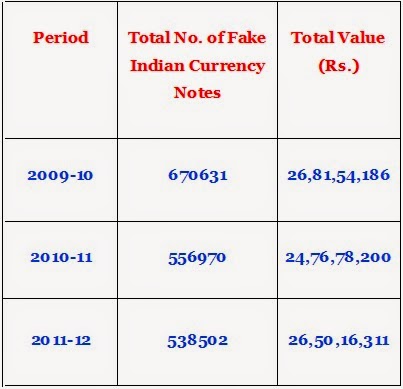
The sustained efforts of the Govt and RBI has not gone waste. Though the value of the seized currencies were almost same, there is decline in the quantity of Fake Indian Currency Notes in circulation for the period commencing from 2009-2012 as per the data provided by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
The basic problem on fake notes are that the fake notes in circulation at a given time is neither measurable, nor estimatable correctly due to multiple denominational notes involved and continuous flow of fakes into circulation, at the same time a part of them getting seized here and there in different states spread across the country.
It is interesting to read what Dr M N Buch, Dean, Centre for Governance and Political Studies of Vivekananda International Foundation on the issue of fake currencies mentions. The following are few observations .
According to Dr M N Buch contrary to the estimates of Nayak Committee which was set up by RBI to study the extent of fake currencies, which said that as on 2000 the value of fake currency in circulation in India was to the extent of Rs 1,69,000 crores, the figure as of 2005 could be around Rs 12,00,000 crores.
Dr M N Buch opined that ‘the Fake Indian currency notes principally originate from Pakistan, but smuggled through various routes, using different modalities. Directly, smugglers make best use of train services and commercial trucks that run between Pakistan and India to push counterfeits into India. The most popular indirect routes are via UAE, Nepal and Bangladesh. Fake notes from Dubai are transported through air with the help of bonafide passengers or couriers appointed for the purpose. Thailand, Malaysia, Myanmar and Sri Lanka are also used as transit points. International airports in Bangalore, Chennai, Calicut, Cochin, Hyderabad, Mangalore, Mumbai and New Delhi are identified as main landing points of counterfeits from abroad. Porous and weak land borders respectively with Nepal and Bangladesh are utilized by organized gangs to smuggle fake currency into India. It is also carried by infiltrators from Pakistan. Making use of weak maritime security, counterfeits have also been routed through sea. Once smuggled, the fake money is exchanged for original notes at roughly 2:1 ratio or even higher. Interestingly, there has been a spurt in fake currency circulation especially since 2006, roughly when Pakistan intensified its proxy war against India’.
Dr M N Buch continued ‘To distinguish between fake and real currency notes has become increasingly difficult mainly due to the fact that counterfeits are now printed with state of the art technology using security paper that is made available only to state actors. This clearly indicates involvement of government agencies in the neighborhood. Pumping fake currencies is one of the sub-conventional warfare strategies pursued by Pakistan against India. The objectives behind are to subvert Indian economy and to fund terror networks. According to a Planning Commission Report, the fake currency enables the adversary to obtain the services of individuals and groups in this country to act against our security interests at very low cost to itself. Once such conduits are established, they are used to push in drugs, explosives, weapons and trained terrorists. For instance, investigations reveal that Rs 50 million that was incurred by the terrorists to trigger blasts in Hyderabad in 2007 and Rs three million spent on the attack on the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, in 2005 were generated mainly through fake currency. Apart from security, fake currency poses huge socioeconomic problem. Its impact on general crime on society is serious as more and more educated unemployed youth are attracted towards the counterfeit racket. In short, this can be dubbed as a dangerous facet of ‘economic terrorism’ confronted by India’. (Courtesy – Source: http://www.vifindia.org/article/2012/march/05/Counterfeit-currency-threat-to-india-s-internal-security#sthash.I65mY4mv.dpuf )
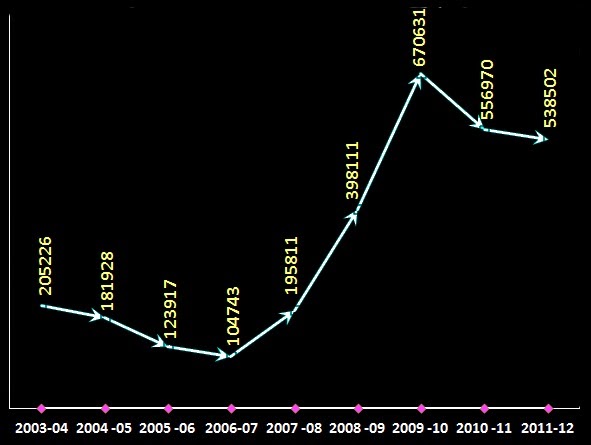
No of counterfeit notes seized during various periods are shown in the following graph :










Recent Comments