
Alphabet – C/3

24. Color Sequence : The order or sequence of printing various colours determine the printed result. Color sequence can vary from each job and the with each printing press though theoretically the sequence is supposed to be Cyan, Yellow, Magenta and then Black shortly termed as CYMK(K for black). However some presses continue to print Yellow first, followed by Cyan and Magenta. The Black colour is always printed at the end. There is no specific sequence that has proved to be optimum in reproducing the image to the exactness of the colored original because each press have their own method of working and the ink they use is mostly non standard and procured from different sources. The reproduction of colored original depends on several such factors as stated above.
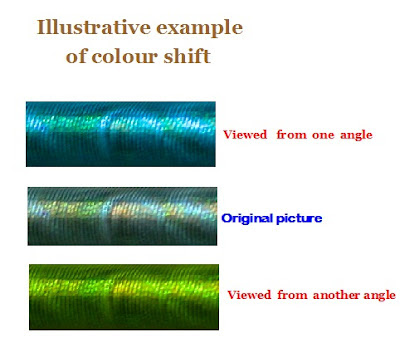
25. Color Shift : Change in image color resulting from changes in register, ink densities or dot gain during three to four-color process printing. This apart change of color shades visible to the human eye when the printed matter is turned in different angles also falls under this category. One classic example is color shifting inks called Optically Variable Inks (OVI) and colour threads used in some of the Currencies or Bank notes to create multi-colored effects when viewed from all angles. If such OVI printed or color shift threaded Currency or note is slightly bend downward or sideways, one can see the colours showing differently in each direction. The holographic images are also another example for colour shift .
26. Composite Proof : Errors corrected final proof showing actual colours of the reproduced original with graphics and matter in their respective places as per the approved layout .
27. Composition : This term should not be confused with the term composing which is nothing but composing the matter either by mechanical means or by hand for letterpress printing process. Composition means assembly of the composed matter in a format incorporating the elements of graphics wherever needed in the text so that they can be processed for printing after completing subsequent operations meant for each processes.
In the case of Offset and Gravure printing this work is done by the layout artist after the main text matter is composed to a preset size . He will paste the text matter in position along with graphics and register marks so that negatives or positives can be straightaway taken to prepare a plate for printing.
In the case of letterpress printing, the text matter is composed either by mechanical or hand composing and then they are assembled in special frames along with the blocks containing graphics into required page sizes and made ready for printing. Both the actions carried out for Offset and Letterpress as narrated above are called composition.
28. Continuous-tone : An image, such as a photograph, where the gray levels in the image are continuous and not drastically varying from one shade to the other like cut colour. The continuous tone image will have virtually unlimited range of shades of grays, starting from white to dark greys and lastly black merging into the neighboring areas in a smooth flow. The term refers to photographs and illustrations having a range of shades from white to black but not made up of dots. The originals which have images drawn in lines and dots and other broken graphics will not be called continuous tone copy.


29. Copy board : Surface or frame on a process camera or enlargers that holds original copy in position for further processing.
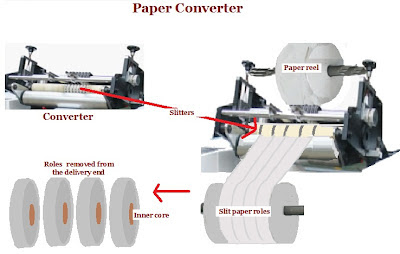
30. Converter: The process by which the reel of paper is trimmed to specific sizes of sheets or roles. This is done basically in the paper mill by separate automatic slitter or slitter cum trimming machine before supplying paper. However some units buy the jumbo roles of paper and get them converted to different sizes to suit their regular work as paper mills can not supply small quantities in different sizes as it will not be economical to handle smaller quantities. The converter machines are mostly used for trimming the jumbo roles into smaller width roles of different sizes specially to print labels etc in a web press.
Unlike the guillotine or cutting machines, in the converter machines bunch of sheets are not trimmed to size, but only the paper from the continuous reels are cut to required size by special cutting blade called slitter instead of heavy cutting machine knives which fall flat on the sheets stacked for trimming. The cutters called slitter in the converting machine slits the paper into desired width and the slit paper gets rolled on to another cylinder containing several inner cores sleeved over it . Once the slitting is completed the rolls will be taken out along with the inner core .
Also the box making and wrapper making machines come under this category as they convert the plain sheets of paper or boards into certain shapes.
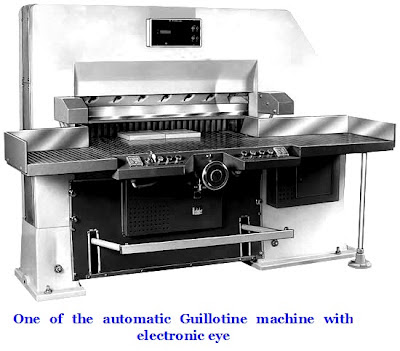
31. Cutting Machine : A machine that cuts stacks of paper to desired size. Every press will have a cutting machine to process both the plain paper prior to printing, and to finish the printed paper into required size. The cutting machines are also called Guillotine machines. Now automated, electronically controlled Cutting/Guillotine machines are available which when per-programed with required data like cutting the multiple up printed stocks to specific length, they keep automatically moving the stacked paper to precise position till the final edge is trimmed. The electronic eyes fitted on such machines will stop the machine if some interference occurs while trimming take place. This is meant to guard against accidents.
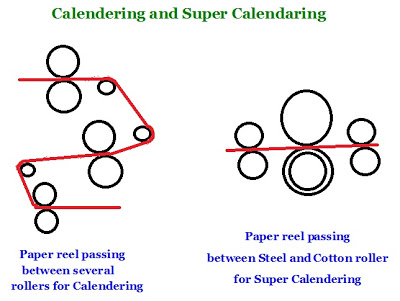
32. Calendaring: Calendaring of paper is finishing process designed to smoothen its surface so as to improve gloss as well as printability as different kinds of papers are needed for different types of job. Due to the pulp formation on the surface of the paper which to some extent have roughness, the paper will be required to be passed under a set of highly polished steel rollers to smoothen the surface. Called Super Calendaring it is the end operation on the paper making machine. The paper is drawn between a series of steel rollers of varying hardness and composition to cause effect something like heat ironing to give smoothness and gloss. Non calendared paper will have less smooth texture. Non calendared paper will be porous and have uneven surface. Since the thickness of the paper also fluctuates in different areas causing uneven surface and higher poracity which increase the consumption of printing ink, it also decreases the printing quality to some extent.
In calendaring process the paper surface is compressed thus smoothening it as it passes between set of rollers. The effect of getting smoothness on the paper depends on several methods deployed for this purpose. Paper passing under several rollers, some of which may be heated rollers, hard rollers and soft rollers etc are some to cite as example.
In the case of Super calendaring of the paper, it is done by passing the paper between stainless steel and soft cotton cylinders under high pressure. The surface of paper can be glossy or matte, smooth, silky, rough, or something in between. This term should not be confused with coating of the paper in the paper mills which is done using certain coating substances. Coating and Calendaring are two different processes.
33. Cartographic Printing: Cartography is the science of producing maps. Printing of Cartographic maps are very delicate and a specialized subject as slight mis-register can alter the data reproduced especially where the maps are made to certain scale to sizes. Most of the map Printing is handled by Survey of India Presses who have specialization in this art.
34.China Clay: Kaolin, a clay mineral called china clay is used by paper makers to give smooth finish and consistency on the paper surface. Most of the art and chromo papers are coated with china clay. Paper could be coated on either or both sides. Paper coated with china clay or other fillers give a smooth surface thus making them suitable for the printing of fine details. China clay called filler or loading agent when used as coating agent improves the paper appearance by contributing to brightness, smoothness and gloss. It also improves printability.
35. Cross direction : The direction of fibers floating across the grain. In simple word, the direction of the floating fibers is at right angle to the machine direction fibers. Paper is weaker and more sensitive to changes in relative humidity in the cross direction than in the grain direction known also as machine direction.
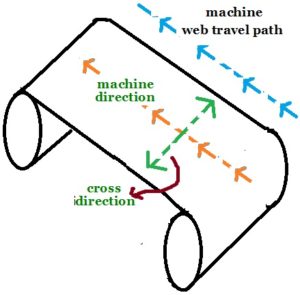
While converting the reels to sheeting, the machine and cross direction are to be kept in mind and the sheet cutting done to suit the end use requirements since they influence registration, dimensional stability, creasing and folding properties.
36.Colorants: This is an important term in the ink making. Colorant or the pigment influences the visual appearance (colour) of an ink.









Recent Comments