1. Foil: A thin film made of metallic, plastic or other similar material which will be used like ink in foil embossing and foil stamping. The foil also comes printed with several designs. They are also used by food packaging industries. Read more under foil stamping below.
2. Foil Emboss: A process of embossing foil onto a substance using a special male- female combination die and heat process. They are replacement for gold or silver embossing. Read more under foil stamping below.
3. Foil Stamping: A common process of pressing or heat pasting foil onto a substance using a die. Such work is done generally to enhance the glitter of a specific portion in a design. This is a finishing technique done after printing. Since the images are transferred from a sheet of metallic film, no inks are used. It is specialized procedure by which with the combination of heat and pressure different shiny designs and graphics are stamped on to the surface of various materials. Foil stamping gives the stamped design a shiny and beautiful look . Where high quality of reflective image is required, it can be achieved by using foil films rather than using shiny metallic inks to print the images. The foil stamping will make the print appear as though some highly polished metal has been embedded on the surface. This process is not complicated and simple technique is involved. All that one would need is a deign engraved die with the image in relief, a pressing machine and heater to heat the die to a low degree which is required to release the metallic foil from the base film to enable the foil stick to the surface on which it is foiled. Coated stocks of papers are the best paper suitable for foil stamping.

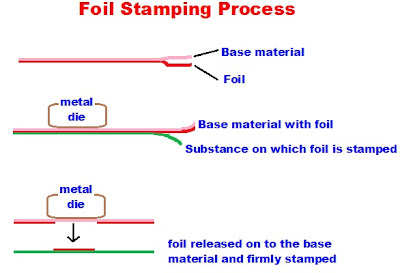
There will always be a confusion with two similar terms- Foil embossing and Foil stamping. For foil embossing a male-female combination of die is used. For foil stamping, only a male die is used to press the foil onto the surface aided with heat. In addition to paper stocks, the foil stamping is commonly done on leather products like valets, fancy bags, greeting cards, visiting cards, invitations, souvenirs, annual reports of high value etc. The only limitation to this process is that multi colored designs can not be reproduced by foil stamping. If however multi colored images are pre-printed by digital process on the foils, they can be transferred but this process will not come under foil printing. These days automatic foil stamping machines are also available.
4. Four Color Process: A multi colored image of the original is reproduced by the printing process using four color inks like cyan, magenta, yellow and black . This term will not be applicable to the digital printing where the color reproduction of the original is done using four color cartridges which creates the image in one go. In the case of printing by four color process, four sets of negatives or positives are first prepared followed by plates or blocks and then printed on the machine one color followed by another color.
5. Fast Color Inks : Inks that retain their original color strength and resist fading as the product is exposed to the light quite often and also retain original density i.e is color strength even when washed when printed on washable material surfaces.
6. Feeder Unit : There are four types of feeders fitted on a printing machine. They are called:
- Fiction Feeder
- Sheet suction Feeder
- Continuous suction feeder
- Continuous reel fed
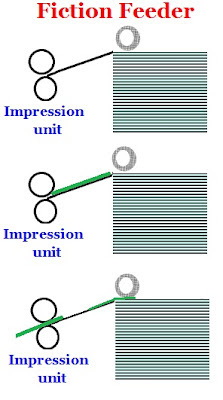
The fiction feeder pushes the stacked paper one sheet after the other. Only after the first sheet pushed by the feeder enters into the impression unit and held by the gripper, the next sheet will get pushed. This type of feeders are almost defunct now on the printing machines and can be seen only on duplicators and photo copying machines.
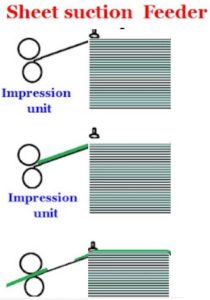
In the case of suction feeder too the same principle is applied. However instead of the pusher, the front edge of the sheet is sucked by some suckers and moved in to the impression unit where they will be taken by the grippers. Only after the sheet thus forwarded is taken by the grippers, the second sheet will be sucked and moved forward. In other words till the tail edge of the paper is moved away from the feeder board, the subsequent sheet will not be forwarded. They are also called cut sheets feeder, a mechanism that holds a stack of paper and feed only one sheet at a time. These feeders are still used on the small sheet fed printing machines of both Letterpress and Offset machines.
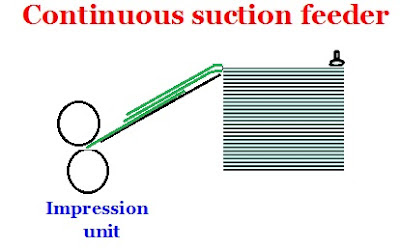
In the case of continuous feeder the back top edge of the sheets will continuously be sucked and forwarded to travel one below the other with a small gap in distance in front edge of the sheet. The sheet travel will be organized in such a manner that the front edge of the subsequent sheet will reach the impression cylinder gripper only after the first sheet gets gripped and entered into the cylinder impression cylinder. Also note that the continuous sheet feeders will have multiple rows of cylinder grippers to keep taking the forwarded sheets in continuous action.
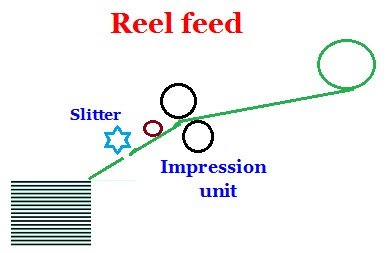
In the continuous reel feeder, the reel of paper is loaded which continuously move and get the impression on the reel, which then will be slit into sheets at the end of the delivery after printing.
7. Felt Finish Paper : The paper surface having soft felt like finish. This is one of the varieties of un-calendered paper with their surface finished with some texture effect with woven wool or synthetic felt material. This variety of paper is meant for printing text matters like brochures to letterheads. The surface gives velvety look.
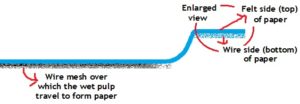
8. Felt Side : This is term is used in the paper making process and refers to the side of the paper that was not in contact with the wire side of the paper making machine . It is usually smoother than the bottom or wire side and is generally the preferred side for printing. The felt side of the paper also comes in contact with the dandy roll during water marking. The bottom side of the paper, which comes in contact with the wire forming fabric of paper is called the wire side. The felt side of a paper may appear to be softer, while the wire side of a paper may have some amount of roughness on its surface. It is general opinion that due to the softer texture of the felt side of an uncoated paper it may pick up slightly more ink than the wire side of the same sheet to maintain the density of color and the printer may have to adjust ink densities to compensate for this. The felt like finish can also be accomplished by an offline process after the paper is manufactured. However neither the felt finish nor the non felt finish paper will affect the strength of the paper. Paper is generally packed with their felt side on top.
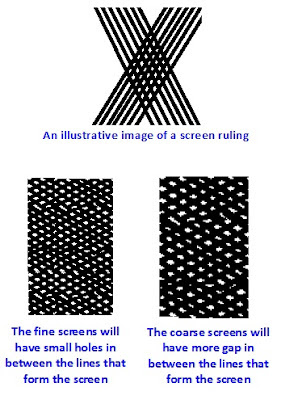
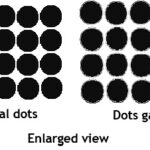
9. Fine Screen : This term is applicable both in Process reproduction as well as Silk Screen printing. The continuous tone originals are converted into printable form by the use of something called halftone screen. The halftone screen breaks the tonal values (shades) into minute dots of varying sizes while preparing negatives through process camera. The halftone screens are made up of fine ruling of lines that cross each other leaving small gap between them. Such screens are made with different screen rulings for use. The resolution of a halftone screen is measured in lines per inch which is indicated by the term ‘lpi’. Therefore the resolution of the screen is written as “150 lpi” or “150#”. For finer work fine ruling screens such as 250 lpi and up to 400 lpi are used.
…………Additions to alphabet F to be continued under F/2

















Recent Comments