
Alphabet – C/2

15. Computer-To-Plate: Called CTP, by this technology the design to be printed is directly transferred on to the plate by digital process eliminating the traditional use of process camera in which the negatives or positives are first prepared followed by plate making process to make ready a plate for printing. Earlier the direct computer to film technology called CTF, was introduced to directly prepare the negatives or positives from the originals without intervention of process camera followed by the development of CTP by which even preparation of the plates for the Intaglio process was made possible. While processing of negatives and positives and plate making process were eliminated for the production of direct printable plates by Dry Offset process, in the case of Intaglio process of printing, the images are directly engraved on the Intaglio plates. This eliminated the manual hand engraving process in which a master die had to be first prepared engraving on a metal plate from which several moulds were taken, assembled and master plates prepared by electrolysis process. From the master plates thus prepared multiple plates for printing by Intaglio printing machines had to be made.

17. Cover Paper: Heavyweight paper that is commonly used for printing book covers, file folders, presentation folders, greeting cards, business cards, postcards, brochures. The cover paper comes in different qualities, thickness, finish and colors to match the printed book paper colors and finishes.
18. Crop Marks: This is nothing but marks meant for guiding trimming area. They are printed as lines , cross marks etc at the edges of a printed sheet indicating where the paper is to be trimmed. Some of the printers prefer to use the crop marks as register marks instead of separately using a register mark.

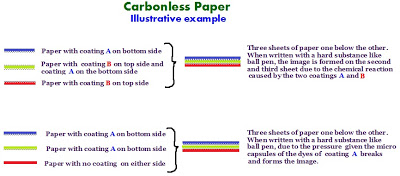
19. Carbonless Paper : Special variety of paper coated with chemicals on their back side to produce second or third copies with pressure from writing or typing thus avoiding use of Carbon paper for making multiple copies. The paper is coated with micro encapsulated dye or ink or some sort of reactive clay for this purpose. However the coating will remain invisible to naked eyes. With pressure from the tip of the pen or typewriter keys, the micro-capsules of color dye breaks and form images by a chemical reaction with the color acceptor on the surface of the front side of the front side coated sheet below. These paper eliminates the use of carbon ribbon or carbon paper thus increasing the efficiency of the user as time wasted in keeping the carbon paper in between sheets, then removing them etc are saved. These are used by business concerns to produce duplicate, triplicate copies in the business deals.
20. Chalking : This is one of the defects attributed to Ink-Paper relationship. The images on the printed stocks appear to fade away or show dusty image after the sheets are printed. The deterioration on the printed image is caused by ink carrier vehicle that gets absorbs into paper too fast leaving the ink pigments in semi wet condition on the paper surface or are not getting properly absorbed into the paper thus causing improperly-dried ink getting rubbed off from the surface of the paper. This powdering defect is due to the ink that has not been properly formulated to suit the paper. The other possible reasons for this defect could be acetic paper, fountain solution too acetic (in wet offset ),too soft an ink which emulsifies etc.

21. Coarse Screen : This term is applicable both in Process reproduction as well as Silk Screen printing. The continuous tone originals are converted into printable form by the use of something called halftone screen. The halftone screen (Read further under Halftone Screen) Halftone screen breaks the tonal values into minute dots of varying sizes while preparing negatives through process camera. The halftone screens are made up of fine ruling of lines that cross each other leaving small gap between them. Such screens are made with different screen rulings. The resolution of a halftone screen is measured in lines per inch which is indicated by the term ‘lpi’. Therefore the resolution of the screen is written as “150 lpi” or “150#”. The term Coarse screens refers to screens having 65, 85 or 100 lines per inch. For finer work fine ruling screens such as 250 lpi and up to 400 lpi are used.

22. Color Separation : Color separation is the process by which original color artwork is separated into individual color components for printing in certain sequence. The components are cyan, magenta, yellow and black, known as CMYK. By this process the colored originals are first converted to printable image using a process camera or a scanner.
Though traditionally process color separation has been carried out using different colour filters (read more under colour filters), the said traditional manual process is being replaced slowly with electronic scanners. Four halftone negatives are prepared to print yellow, cyan, magenta and black colors to render the true colour image as per original copy. In order to achieve it, four separate negatives or positives to print yellow, cyan, magenta and black colors are made using colour filters.
- The yellow filter is used to make a negative to print Black colour.
- The Red filter is used to make a negative to print Blue (Cyan) colour.
- The Blue filter is used to make a negative to print Yellow colour.
- The Green filter is used to make a negative to print Red (Magenta) colour.
Since the colour separated negatives or positives will not be defect free, the negatives or positives are manually corrected wherever it is necessary to bring it closer to the original before final negatives or positives are made. However in the scanners, this correction is automatically done as the original is read by the scanner and necessary corrections automatically carried out to produce color separated negatives or positives.










Recent Comments